Why EV charging security matters
The electric vehicle (EV) revolution is underway — and in Europe, it’s accelerating fast. With ambitious targets for phasing out internal combustion engines, EV charging infrastructure is booming. But more charging stations means more opportunities for frauds and cyberattacks.
For too long, many EV-charging systems have relied on nothing more than reading a 13.56MHz card ID (UID) to authorize charging sessions. Unfortunately, this is no longer secure. Tools like Proxmark, cheap MIFARE “Magic” cards, and other hardware hacking kits make it trivial to spoof or clone simple RFID credentials.
To address these issues, Germany’s major actors of the field have developed the VDE-AR-R 2532-100 standard. This standard defines a robust protocol based on digital certificates and ECDSA signatures to authenticate cards beyond doubt.
The new MIFARE DuoX chip from NXP (code name MF3E(H)x3) is the first widely available card that supports this new standard and paves the way for tomorrow’s state-of-the-art in terms of security level. The MF3E(H)x3/01EV version of this contactless smartcard comes pre-provisioned with an ECC keypair and certificate issued by NXP’s CA, and is capable of speaking the VDE-AR-E protocol out-of-the-box.
SpringCard’s VDE-AR-E reader script
At SpringCard, all our contactless PC/SC couplers (like Prox’N’Roll, M519, SpringPark, PUCK, etc.) are already fully compatible with VDE-certified MIFARE DuoX cards.
To help integrators, we’ve created a ready-to-use Python script that:
- Selects the correct VDE application on the card
- Reads the card’s certificate and metadata
- Issues a random challenge and verifies the ECDSA signature computed by the card
- Confirms that the card is authentic (certificate validity, key usage, signature consistency)
With this script, you get a solid foundation to integrate secure card authentication into your EV charger backend.
Whether you’re using a mini-PC or an embedded Linux board (like a Raspberry Pi, Jetson Nano or industrial box), this script gets you started on the right foot.
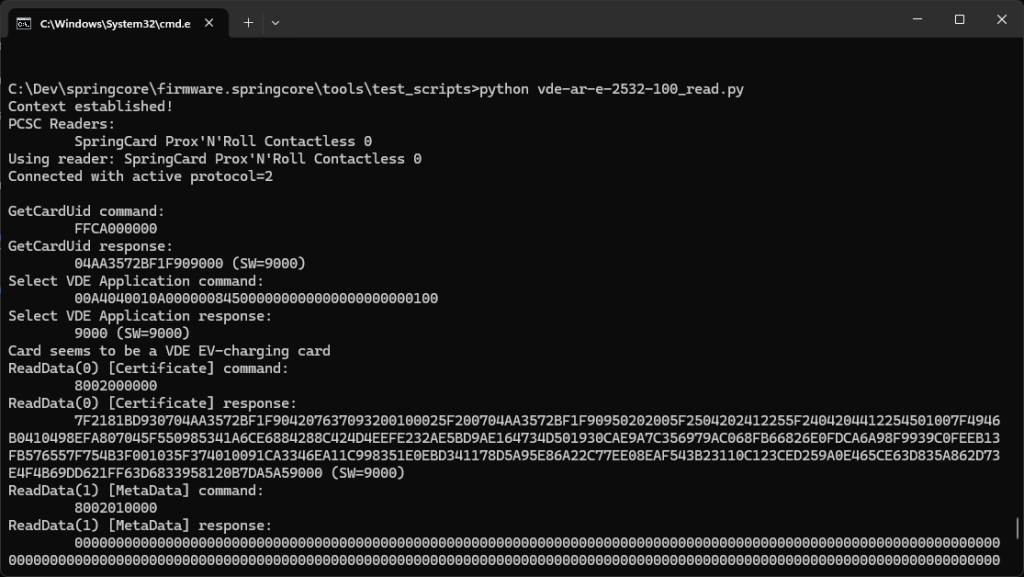
Under the hood: VDE-AR-E Card processing explained
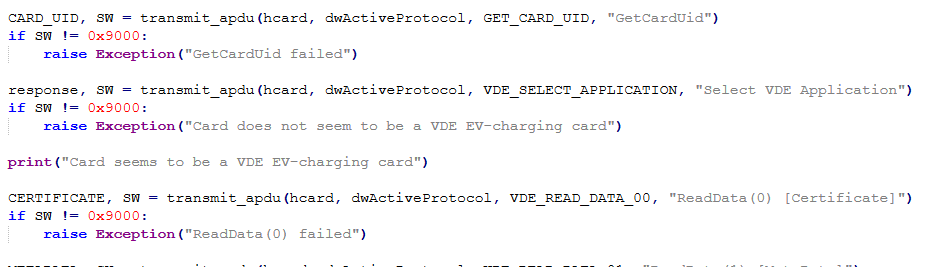
The APDUs
We interact with the card using standard ISO/IEC 7816-4 APDUs:
SELECT APPLICATION: selects the VDE AIDREAD DATA(0): retrieves the certificateREAD DATA(1): retrieves metadata (optionally empty)ECDSA SIGN: asks the card to sign a random challenge
Each APDU is wrapped and transmitted via PC/SC using the pyscard Python module.
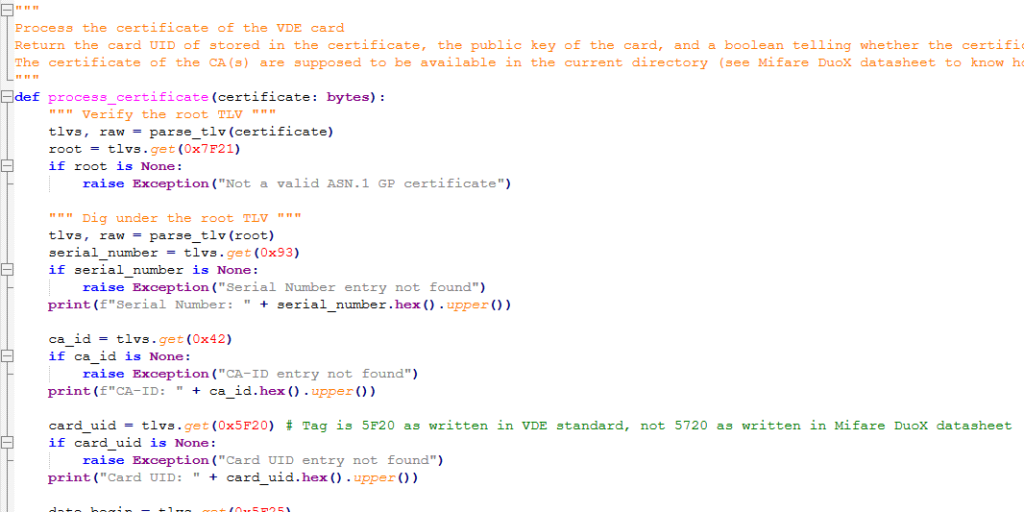
Parsing the certificate
The certificate retrieved from the card is encoded in ASN.1 DER, but uses a GlobalPlatform format (not X509!). We use a quick parser to extract fields like:
- Card UID (Tag 0x5F20)
- Serial Number
- CA ID
- Validity dates
- ECC Public Key
- ECDSA Signature
We also check if the CA certificate is available locally and attempt to validate the certificate signature using Python’s cryptography module (the CA certificate provided by NXP is X509 DER).
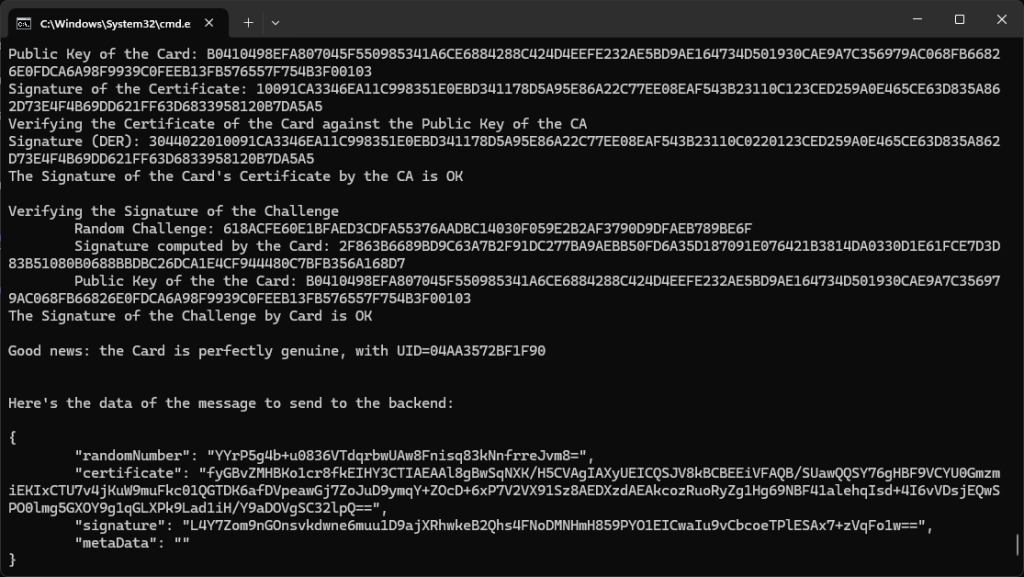
Veryfing the card authenticity
Once we have the card’s public key, we:
- Generate a random challenge
- Ask the card to sign it
- Verify the signature using the card’s public key found in its certificate
If all these steps succeed, and the UID in the certificate matches the physical UID of the card, then we have strong proof that the card is genuine and uncompromised.

What’s next?
With this script, you’re now able to:
- Authenticate EV-charging cards in compliance with VDE-AR-E 2532-100
- Work with MIFARE DuoX cards, either pre-provisioned by NXP or personalized under your own PKI
- Feed your backend with signed credential data for session validation, authorization, and billing.
Are you building EV-charging stations and using this script in production or maybe just for test?
We’d love to hear from you! Share your feedback, tell us how the integration went, or even better, send us some photos of your setup. You can reach us via support@springcard.com or tag us on LinkedIn. Let’s shape the future of secure EV charging together.
Download
The VDE-AR-E-2532-100_Read.py Python script here:
(the extension is .txt to please some paranoid security tools, change for .py and chmod +x to allow execution)
The certificates of NXP’s EV Charging CA can be retrieved via the following link: https://www.gp-ca.nxp.com/CA/getCA?caid=63709320010002 . Save it under the name 63709320010002.crt in the same directory as the script.
